Living with HIV: A Diagnosis is no Longer a Death Sentence
March 31, 2021

Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a sexually-transmitted disease that attacks the body’s immune system by destroying cells that fight infections and diseases. While there is currently no cure for HIV, advances in treatment mean a diagnosis is no longer a death sentence.
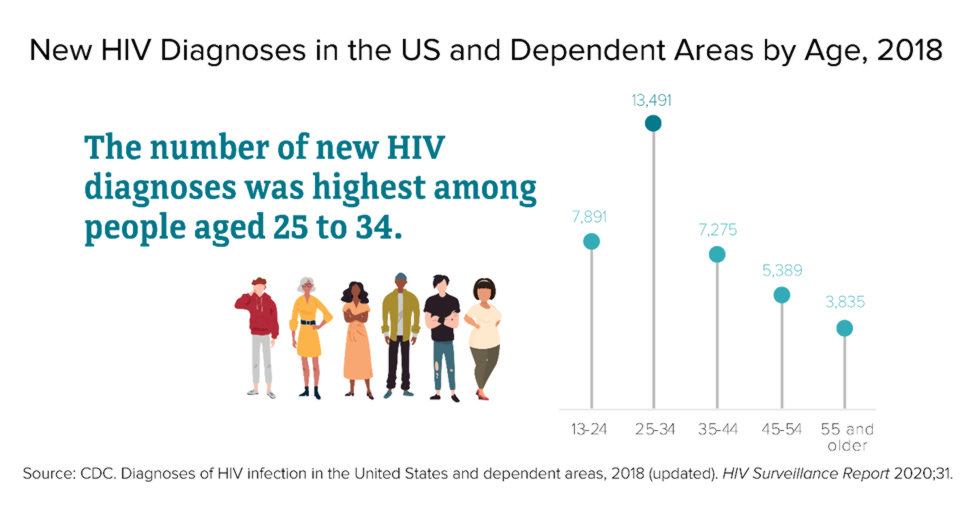
HIV is most prevalent in people aged 25 to 34. It is also more prevalent in the south, and Texas ranks 3rd on the CDC’s list of states with the highest number of new HIV diagnoses. If you are sexually active, protect yourself and your partners by using protection during every sexual encounter.
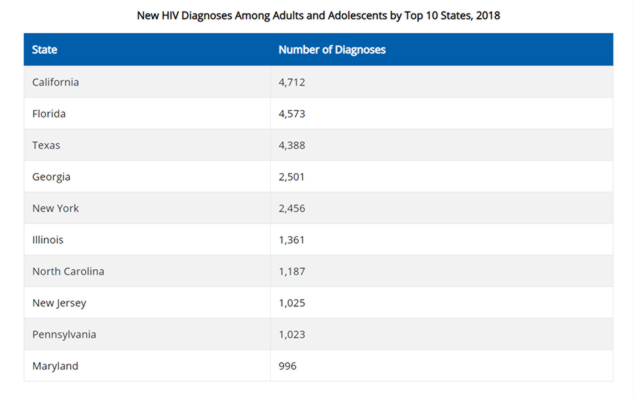
(Graphic source: CDC)
The Importance of Getting Tested
The CDC recommends everyone between the ages 13 – 64 get tested for HIV at least once as part of your routine health care.
As is the case with other STD’s, if you are sexually active and not in an exclusive relationship, you should get tested regularly to protect yourself and your sexual partners.
Living With HIV
The prognosis for people diagnosed with HIV has changed drastically over the years. “Today, HIV is considered a treatable chronic disease much like diabetes, high blood pressure or high cholesterol,” said Texas MedClinic Chief Operating Officer Dr. David Gude. “Medical research and pharmaceuticals have completely changed the HIV prognosis. For example, in 1996 a 20-year old diagnosed with HIV could expect to live to 39. Today, a 20-year-old who is HIV positive can expect to live to an average age of 71, very near the 79-year average life span for a person living without HIV.”
If you test positive for HIV, it is imperative that you:
- Find an HIV healthcare provider – This may be your regular healthcare provider or one who specializes in HIV care.
- Begin treatment as soon as possible – You must begin antiretroviral therapy (ART) which can reduce the amount of HIV (or viral load) in your blood. When taken correctly, ART helps you reach and maintain an undetectable viral load, which means you cannot transmit the virus to others. It usually takes 6 months of HIV treatment to get the virus under control.
- Follow a healthy diet – Nutrient-rich food helps your body fight HIV
- Get regular exercise – Exercise is great for both physical and mental health. Regular exercise reduces the risk of developing depression and strengthens your immune system.
Where to Find Help with HIV Testing & Treatment
- Find HIV care services near you
- Find your state’s HIV/AIDS toll-free hotline
- Search HIV care specialists




